By Raul Bernardino
Introduction:
Today global
communication has become an easy to communicate and become a complex to control.
Moreover, it has become a huge issue on data migration whereas without any boarder.
Nobodies know exactly known with whom they are connected. Either, they are
connected to the right and wrong infrastructure or a person. Nobodies can
guaranty, that their networks and systems are most secure than the others.
Ethical hacking is a
science of the computing security in which is to test the vulnerability of
his/her networks or standalone personal computer (PC). The technical person
will be closing all open ports or plug all other systems holes before the bad
person is trying get into system and attack the networks or the individual PCs.
Several ethical hacking
whereas sometimes are hard to define. Either, they are still in an ethical corridor
or they are in the hacker parts. There are several types of ethical hacking
that can be explained the differences between ethical hacking and hackers.
Moreover, before we
talk about the ethical hacking issues, there are several fundamental elements,
that we need to know. They are: the important issue of the security in the
system, several elements of the security, to see phases of the hacking, etc.
Why should we talk
about the importance of the security? It is because, in today technologies are intending
to be an easy for the users to be used, the technology and the complexity of
the network in which we have no ideas whereas the level of the security, either
it is secured or not. There is a triangle model (annex: picture 1) in which can explain about the three component of
the technology. They are functionality, security, and easy to use. If the
technology is focusing on “easy to use” then there would be less functionality
and security. Same as if the technology is focusing on the functionality, there
would be less secure and more complex of the using the technology and so on so
for.
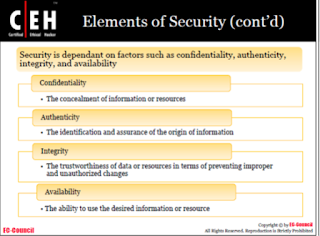
The elements of the
security are: the data integrity, the confidentiality of the information,
authenticity, and availability of the data. (Annex: picture 2)
Additionally hacking phases are:
starting from recognizing, scanning, gain the access, maintain the access, and
clear the track. (Annex: picture 3)
“White
hat cracking”:
This is a first type of ethical hacking in which is involving a security test
to the network system or standalone PC with an agreement upfront or with the
signed contract arrangement. This is ensured the scope of testing produce, a
report, and recommendation.
“Grey
hat cracking”: This
is a second type of ethical hacking in which without establishing an agreement
upfront before he or she is assessing the target system environment and
possible to identify the vulnerability of the system. Additionally, they will
be reporting or informing the facts to the system administrator or network
administrator to know the status. This type sometime can be become white or black hat.
“Black
hat cracking”: This
is a third type of ethical hacking in which is involving to access the systems.
Anyone can determine that black hat
is immoral. However, it is depending on the target. If black hat is after gain the access he/she is intend delete some information
or controlling the information then it should categorize as crime. The black hat has more knowledge on how to
cracking a systems and find the possibility to prevent hacker then he or she
doing a good job. The black hat is also
able or have the ability to make counter-attack of phishing on server, spam,
etc.
“Hacktivism”: This
is another type of the cracking or hacking; however, this one has higher level
of purpose of cracking the system. For instance, it has
political agenda behind the attack. The cracker is sending a message to target
attack that they are able to do so.
“Is it possible to crack systems and still be ethical? Support your position”.
“Is it possible to crack systems and still be ethical? Support your position”.
My answer would be two:
Yes, if the crackers are in the corridor of white
hat, grey hat with the condition of reporting to the target, and black hat with ability to counter-attack
the phishing and plug all holes.
No if the crackers like
grey hat is not informing the issues
finding to the target and back hat
use his/her ability to delete some information on the target or control the
target. Whatever is the reason to gain unauthorized access is crime.
Conclusion: As a computing professional, we have to have a
responsibility in every activities of hacking. In this sense, either you are a
white hat, grey hat, or black hat it does not a matter.
Annex:
Picture 1: Triangle
from Module 01 v 6.1 of CEH P.12
Picture 2: Element of
Security from Module 01 v 6.1 of CEH P.11
Picture 3: Phases of
hacking from Module 01 v 6.1 of CEH P.14
Reference list:
·
Adams, A.A. & McCrindle, R.J. (2008) Pandora’s box: Social and professional
issues of the information age. West Sussex, England: John Wiley & Sons,
Ltd. Ch 11, P. 366-369